Canonical Classes
CDRs are classified in abYsis using sequence rules which specify loop length and permitted amino acids at required positions. In this way classifications can be made for all numbered sequences, whether or not structural data are available. Use the Region dropdown to select a particular CDR.
Three separate CDR classification methods are implemented within abYsis. These differ in the key residues allowed at different positions. Use the Canonical Method dropdown to select a particular method.
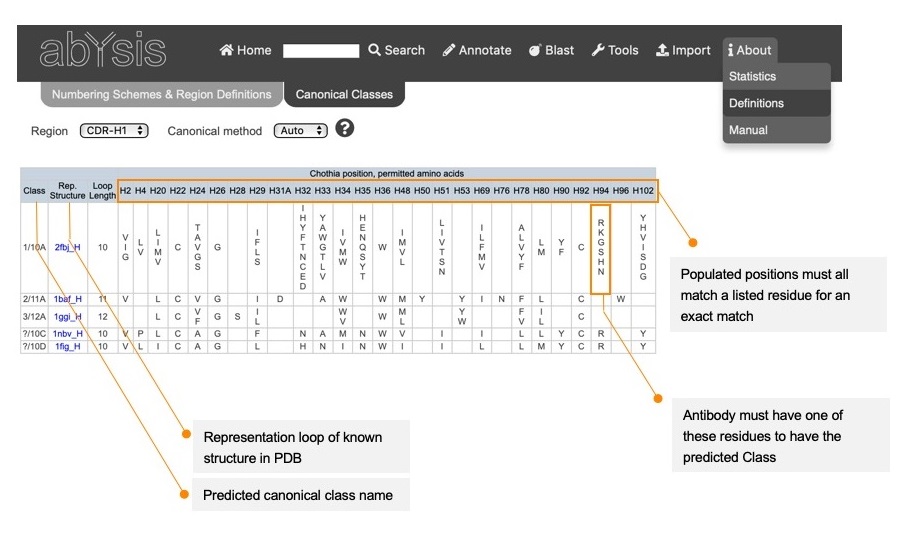
The table shows details of the sequence rules for all the canonical classes corresponding to a particular CDR/method combination.
Chothia position, Permitted amino acids.
For each Method, positions important for a prediction a CDR conformation are listed
- First column shows the predicted canonical class name.
- Second column shows the accession for a representative structure in abYsis.
- Third column shows the required loop length (AbM definition).
The following columns show the permitted amino acids at each required position. These will vary depending on the Canonical Prediction method.
- For an exact match, loop length must agree and the amino acids at each required position must match one of the permitted amino acids.
- For a similar match, loop length must agree but one or more positions might not match one of the permitted amino acids.
Canonical Prediction Methods
Auto Method
- Likely to give the most accurate results as based on strict templates derived automatically from available crystal structures.
- Templates generated using automatic protocol involving cluster analysis and analysis
of buried hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding residues
(Martin and Thornton, J. Mol. Biol. 263(1996),800-815). - Canonical class identifier :
- Equivalent Chothia class followed by a structural cluster number consisting of the loop length followed by a letter to describe the individual cluster.
- Where there is no equivalent Chothia class, a '?' appears (e.g. for CDR-H1, there are classes ?/10C and ?/10D).
AbM Method
- AbM key residues are based on Chothia templates
(Whitelegg N & Rees AR, Protein Eng. 13(2000),819-24 and Methods Mol. Biol. 248(2004),51-91). - Classes are expanded from the Chothia definitions: some additional allowed residues
have been specified together with additional required residues and extra classes.
Classes with a * in the name are not defined by Chothia. - Modifications and references are detailed for each class.
Strict Method
Strict application of templates derived from papers by Chothia et al.
Note
- There are some confusing discrepancies in the canonical class numbers used by Chothia.
- For example CDR-L1 Class 5 is used in earlier papers to refer to a 13-residue lambda light while later papers use class 5 for a 15-residue kappa. Similarly CDR-L1 Class 6 is used in earlier papers to refer to a 14-residues lambda, but later papers use class 6 for a 12-residue kappa. We have used the earlier class numbers.